Data Traceability's Blockchain-Led Revolution
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Data Traceability
- The Necessity of Data Traceability
- Challenges in Achieving Data Traceability
- Overcoming Organizational Changes & Cultural Shifts with Smart Contracts
- Use Cases in Blockchain-Based Data Traceability
- Blockchain: A New Paradigm for Data Access
Introduction to Data Traceability
GDPR and HIPAA set the gold standard for data privacy, compelling businesses to elevate their data traceability strategies.
Even so, companies implementing data traceability often embark on a much larger journey than initially expected. Incompatible tooling, expensive custom integrations, and impactful organizational changes put much stress on organizations wanting to achieve robust data governance and compliance.
Inevitably, these challenges indicate a reassessment of strategies and tools. They push companies to innovate and adapt to meet rigorous standards set by GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulatory frameworks.
This drive towards stricter compliance has led companies to explore new technologies like blockchain. Blockchain inherently fosters trust, as data recorded on a blockchain cannot be altered by anyone. This immutable characteristic makes it an ideal foundation for developing data traceability tools that build on its reliability.
This article looks at the need, current challenges, and potential solutions for data traceability. I will spend some extra time covering the organizational changes and the cultural shifts that need to happen when transforming your company into a data-minded one.
The Necessity of Data Traceability
Data has become the fuel for many companies when making important investment decisions and fine-tuning day-to-day processes. Many companies have hired data scientists or data engineers to help them process and analyze the data they collect.
From my own experience, I’ve seen many companies capturing vast quantities of data yet struggling to derive meaningful insights from it. It’s crucial to have data experts on your team to make data-driven decisions. In the past, our approach was to capture as much data as possible without first considering the specific business questions we need to answer or verifying the accuracy of the data. This oversight often led to data being underutilized and not fully understood.
One of the biggest challenges data-minded organizations face is the need for better data traceability. They often encounter this new problem when scaling their organization or growing the data they capture. The main question they try to answer is: How can we ensure compliance with data requirements like GDPR or HIPAA?
Data traceability is responsible for monitoring data access, data values, and data changes throughout its lifecycle. It ensures that data adheres to its expected process flow, safeguarding that the information is used appropriately and ethically.
So, a clever mind might wonder what the difference is between data provenance and data traceability. Contrastingly, data provenance tries to capture the entire data history from inception. Data provenance ensures data quality and integrity, while data traceability tracks compliance throughout its lifecycle.
Challenges in Achieving Data Traceability
The global compliance and traceability solutions market size was valued at $2.8 billion in 2021. By 2031, this number will reach $9.5 billion, growing at an annual rate of 13.3%.
The space is growing, but why? Here are some core challenges you might face when achieving data traceability.
Integrations
We all love the word “integrations.” It means better business connectivity and more efficient processes. Yet, many of the legacy tools companies still use today are unable to integrate with other solutions. Even if you are using modern tools, this does not guarantee they have the ability to integrate with existing data traceability solutions. This is not an ideal situation because data engineers can’t tell if the data has been accessed or maybe even changed by someone who shouldn’t have had access.
Resource Constraints
Companies that want to achieve data traceability often run into much higher costs than expected, both financially and resource-wise. A common issue is that they must adopt new software or build custom software that can communicate with data traceability tooling. Oh boy, building custom software can be expensive, not to mention the educational cost and the changing processes. Or think about hiring consultants to implement new software. I wouldn’t want to pay that bill!
In short, implementing data traceability solutions can put a lot of pressure on your company’s day-to-day operations.
Organizational Changes
Let’s shed some light on the organizational changes you can’t ignore. Tooling will often change, so the way people work will change.
For example, a marketing team member could access customer information through a data portal. However, they now have to request access to specific customer records and provide a valid reason for using the data.
In this case, data traceability means more complex and slower workflows. These workflows can often lead to frustration among your employees. It’s therefore essential to invest in education and foster a culture that values data traceability, balancing security with accessibility and speed.
To summarize the challenges: High costs, loads of organizational changes, and a fair portion of frustration — cultural changes.
Overcoming Organizational Changes & Cultural Shifts with Smart Contracts
Implementing data traceability can be challenging, especially from a resources and integrations perspective. You can spend a lot of money and resources to build or buy new tooling. And yet, many companies forget the organizational changes and cultural shifts needed to adopt new tooling and processes.
From my personal experience, I’ve found that effectively communicating with employees about how new tooling will impact their work is crucial. Initiating open discussions early on allows employees to contribute insights on integrating new tooling into their daily routines. This approach facilitates smoother transitions and mitigates the potential shock effect when new software significantly alters their workflow.
First, what are smart contracts? They are contracts that live on a blockchain with predefined rules and conditions. Once the contract is triggered, it will execute its logic. The most significant benefit here is that you can’t change the logic of the contract, which is excellent for data traceability as you can be sure nobody has changed the rules of your contract that affect how your data is accessed.
So, how can you use smart contracts for data traceability?
- Automate data access and control policies for applications with data regulations like GDPR and HIPAA in mind.
- Self-Service Portals: Employees can request the data they need without going through a manual validation process.
- Smart contracts can integrate with Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) or Active Directory (AD) to pull up employee profiles, provide automated data access, and log each request.
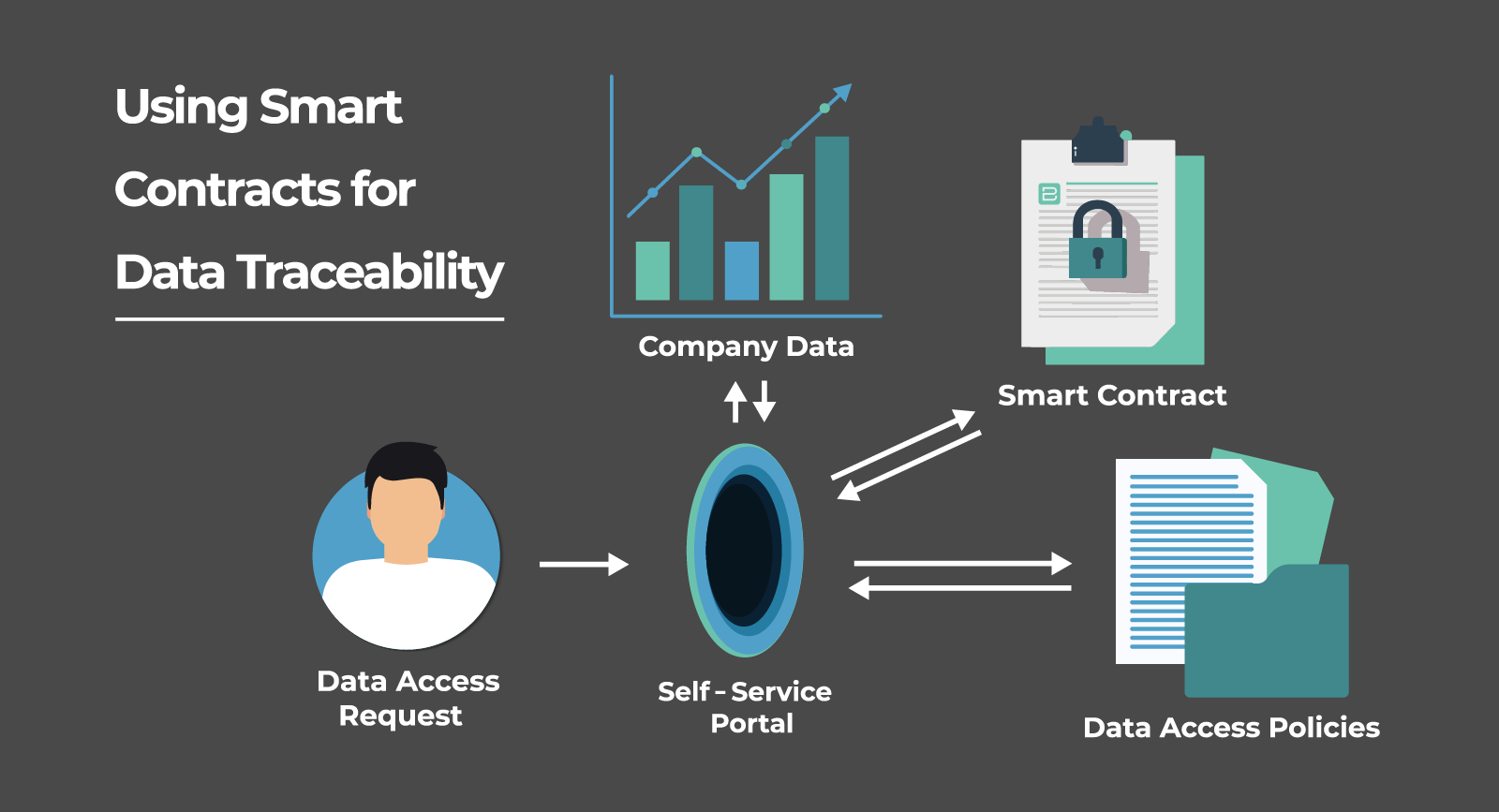
However, you might wonder if smart contracts won’t be challenging for employees to use. When creating a self-service portal, you can simply hide the complexities of blockchain systems. Each employee receives a keypair linked to their employee profile in the LDAP or AD.
The user doesn’t have to worry about key management or interacting directly with smart contracts. The UI should hide all complexities, the user can request data, and the smart contracts will evaluate if the user can access that data. If they can access it, which data they have accessed and when will be recorded.
Use Cases in Blockchain-Based Data Traceability
While discussing smart contracts and blockchain, let’s look at some real-world implementations for data traceability.
Wholechain: Wholechain aims to improve transparency in global supply chains by gathering extensive information along the supply chain. This information helps consumers make informed choices about their food purchases. Additionally, Wholechain enables stakeholders to verify product claims regarding authenticity, legality, and sustainability, thereby ensuring accountability.
mintBlue: Next is mintBlue, who have developed a solution that allows you to store each data access request on the BSV blockchain. To achieve data traceability, you can integrate their product through an SDK or API with your existing tooling.
ECLIPSE Suite: Finally, ECLIPSE Suite allows project managers to trace every data move, data point, and document back to its source. It provides organizations with full transparency into the history of each data point. Their main goal is to improve data quality control, comply with regulations, and increase clients’ trust.
Blockchain: A New Paradigm for Data Access
Can better data traceability tooling increase our collective trust in the digital landscape?
Personally, I remain skeptical. Despite the promise of increased security, the complexity and rigorous demands of safe data handling policies often lead to mistakes. Such policies introduce more work and inflate economic output under the guise of heightened data security.
On the other hand, blockchain can create a future of safer data handling if we can hide all of its complexities from the end users. Smart contracts can be a fantastic tool for automating data access without the user ever noticing they are using smart contracts. That, for me, is a real technological win.
What are your thoughts? Will the advancements in data traceability genuinely make a difference, or are we just masking deeper issues within our digital infrastructures?
